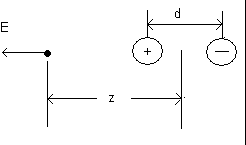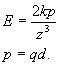|
(Click here
for the lab computations) Theory behind the experiment:
Use the result for the electric field of a dipole as an analogy:
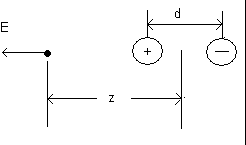
The result for the electric field magnitude E at the location above is:
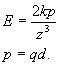
You can get the above result by reading example 25.4 in Ch.25 of the textbook.
The analogous picture for the magnetic field is below:
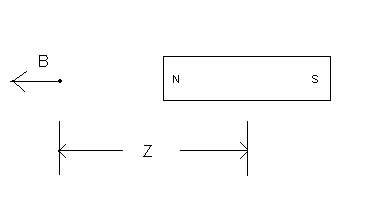
The result for the magnetic field magnitude B at the location above is:
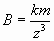
Here m = pole strength of the
"magnetic charge". This derivation is in graduate level physics texts
such Classical Electrodynamics by J.D. Jackson, 2nd Edition, page 182. It was
also derived in out trusty textbook, Chapter 33, to produce equation 33. 9.
The above formulas work when z >>d = dimension of the dipole. When z is so large that
z >>d, the positive and negative charges of the dipole tend to cancel and the power law is z -3. That is why your value of n was close to 3 when your calculation was based on the largest distances 15 cm and 10 cm
(the pair BM1 and BM2) between the compass and the bar magnet. When your calculations
for n were based on averages from the pair BM2 and BM3 and the pair BM1 and BM3, the distances between the compass and the bar magnet were smaller on the average. That why your results
for n were increasingly less than 3.
|